About 3.1% of people in the US face generalized anxiety disorder every year. This shows a big need for good anxiety solutions. Magnesium, often called “the original chill pill,” is vital for mental health. It helps in over 300 body processes every day. These include making energy and sending nerve signals. Yet, many don’t get enough magnesium or use less effective kinds. This makes it hard to handle anxiety and depression.
This guide talks about how magnesium helps mental health, especially for anxiety and depression. Knowing why magnesium is a top pick can help you choose better for your health. For more info, check out this complete guide on the topic.
Key Takeaways
- Magnesium supplements can greatly lower generalized anxiety and stress symptoms.
- Having low magnesium could mean more anxiety and depression.
- Types like magnesium glycinate and magnesium taurate are great for calming.
- The National Academy of Medicine says to stay under 350 milligrams of magnesium daily.
- Millions in the U.S. get generalized anxiety disorder each year, showing the need for better treatments.
Understanding Magnesium and Its Role in Mental Health
Magnesium is key to our body’s function, majorly affecting magnesium role in mental health. It helps regulate neurotransmitters and hormones, important for our mood. Magnesium also helps us manage stress by balancing brain chemicals. Without enough magnesium, people can feel more anxious and stressed.
Importance of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is crucial for many body functions. It helps with muscle and nerve function, and keeps our blood sugar and pressure in check. Adults should get 300-420 mg of magnesium daily. Yet, nearly half of Americans don’t get enough. This deficiency can cause tiredness, muscle cramps, and more anxiety.
Connection Between Magnesium Deficiency and Mental Health Disorders
Research shows a clear connection between magnesium deficiency and mental health disorders. People with low magnesium levels may face more stress and have higher anxiety and panic attacks. Such deficiency may also lead to sleep problems, irregular heartbeat, and other health issues.
A 2017 study found magnesium helps reduce mild-to-moderate depression in adults. Magnesium plays a vital role in mental health, helping us handle stress better. Eating magnesium-rich foods like green leafy vegetables, nuts, and whole grains can boost our levels and mental health.
What is Magnesium Deficiency?
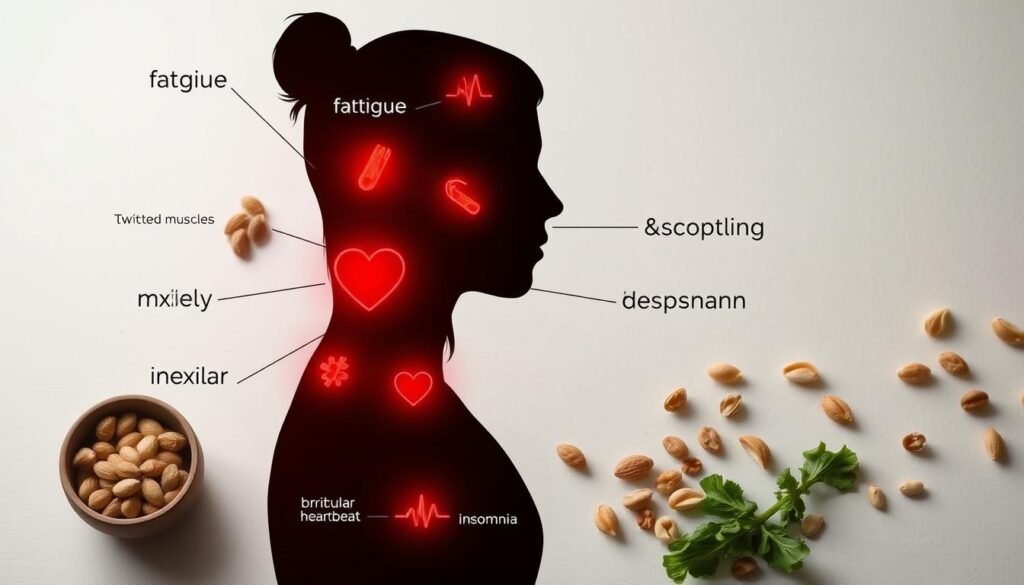
Magnesium deficiency is becoming a major health concern, especially in the West. It causes many symptoms that lower our quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms is key to catching the problem early. It also shows how important it is to eat right and manage our health.
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
When our bodies lack magnesium, we can feel both physically and mentally unwell. We might feel very tired or get muscle cramps. People can also feel more anxious or irritable than usual.
Having trouble sleeping, experiencing digestive issues, or getting headaches for no clear reason are other signs. Spotting these symptoms early can help us change our diet or consider supplements to get better.
How Common is Magnesium Deficiency?
It’s important to realize how widespread magnesium deficiency is. About half of the people in the U.S. aren’t getting enough magnesium. Shockingly, up to 70% of Americans might be lacking in magnesium.
This is often due to poor eating habits, eating a lot of processed food, and soil depletion from farming. These issues make low magnesium levels a growing concern for our health.
| Category | Magnesium Intake Recommendation | Population at Risk |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Adult | 310-420 mg/day | Approximately 70% are deficient |
| Children (9-13 years) | 240-410 mg/day | Commonly insufficient intake |
| Older Adults | 320-420 mg/day | Higher risk due to absorption issues |
How Does Magnesium Affect Anxiety and Depression?

Magnesium is key for mental health, especially for those with anxiety and depression. It works in the brain, affecting neurotransmitter activity and easing the mind. Studies show that magnesium helps manage mood.
Mechanisms of Action in the Brain
Magnesium is vital for brain health as it balances neurotransmitters linked to anxiety. It reduces the activity of stimulating neurotransmitters. It also boosts calming ones. This means low magnesium can lead to more anxiety. In fact, a lack of magnesium is known to worsen anxiety in over 30% of US adults.
Research Supporting Magnesium’s Role in Mood Improvement
Research into magnesium effects on anxiety and depression has been telling. Half of the recent studies showed magnesium reduces anxiety. A 2018 study found magnesium significantly helps those with light to moderate depression. These results highlight how crucial magnesium is for good mood and mental health.
What is the Best Magnesium for Anxiety and Depression?

Some magnesium forms are especially good for lessening anxiety and depression. For the best magnesium for anxiety, look at magnesium glycinate, magnesium taurate, and magnesium threonate. These types offer special advantages for mental well-being.
Overview of Effective Forms of Magnesium
Magnesium’s effectiveness is often linked to how well our bodies can use it. Magnesium glycinate, taurate, and threonate are top choices due to their high bioavailability. They’re excellent for boosting mental health.
Magnesium Glycinate: Benefits and Uses
Magnesium glycinate is known for being easily absorbed and for calming. It’s paired with glycine, an amino acid that improves sleep. Taking 100 to 300 milligrams could help ease major depression signs, offering a way out of anxiety.
Magnesium Taurate: A Calming Option
Magnesium taurate combines with taurine to help the heart and calm the mind. A study found it raises brain magnesium levels more than other forms. Such an increase aids in thinking clearly and lowering anxiety and stress.
Magnesium Threonate: Brain Health Benefits
Magnesium threonate is unique because it can reach the brain easily. It’s praised for boosting brain function and emotional health. High doses, like 1800 mg, have shown to better thinking skills and memory. This magnesium is great for those wanting clearer thinking and stable moods.
| Form of Magnesium | Key Benefits | Suggested Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium Glycinate | Enhances sleep quality and calmness | 100-300 mg |
| Magnesium Taurate | Supports cardiac health and relaxation | 250-500 mg |
| Magnesium Threonate | Improves cognitive function and mood | 1800 mg |
How to Choose the Right Magnesium Supplement
Choosing the right magnesium supplement requires considering a few important things. You must look at the bioavailability of magnesium and what you need for your health. The right supplement can help with issues like anxiety and muscle cramps.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Magnesium Supplement
Keep these factors in mind when looking for a magnesium supplement:
- Individual Health Needs: Look into any health problems you have. Magnesium glycinate, for example, may help with anxiety or depression.
- Absorption Rates: Some forms, like magnesium citrate and malate, are better absorbed than others, like magnesium oxide.
- Recommended Dosages: Dosage differs by form; for adult women, magnesium glycinate often ranges from 200-400 mg per day, while magnesium citrate is typically 100-300 mg.
- Consultation: Talk to healthcare experts for advice based on your health and diet.
Importance of Bioavailability
The bioavailability of magnesium is key to its effectiveness. Supplements that are well-absorbed ensure better health outcomes. For better absorption, magnesium citrate and malate are top choices over magnesium oxide. Those interested in choosing magnesium supplements should weigh these aspects. This ensures their choice matches their health needs and gives the benefits they seek.
Cautions and Side Effects of Magnesium Supplementation
Magnesium supplements bring many health perks. Yet, it’s key to know the possible side effects. Different types of magnesium can affect people in various ways. Some may lead to digestive issues more than others. Learning about magnesium precautions can make its use safer.
Common Side Effects of Different Forms
Here are some usual side effects from taking magnesium:
- Stomach cramping: This often occurs with magnesium oxide, causing stomach pain.
- Nausea: Taking magnesium without food can make your stomach upset.
- Diarrhea: High doses of many magnesium types lead to loose stools.
- Fatigue: It can make some users feel very tired.
To avoid these issues, it’s wise to take magnesium with food. Picking extended-release types might also help ease stomach troubles.
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
Before starting magnesium, talking to a health expert is a must, especially if you have health issues. For example, kidney disease raises the chances of too much magnesium in your body. If you face bad side effects, get medical help right away.
If you’re on other medicines, discuss with a doctor about how magnesium might interact. Knowing when to seek help can dodge serious problems. This way, magnesium can be used safely, improving mental health.
Recommended Daily Intake of Magnesium
Knowing how much magnesium you need is vital for your mental and overall health. In this section, we cover what you should know about magnesium. This includes general guidelines and specific needs for daily magnesium.
General Guidelines for Adults
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for magnesium changes with age and gender. In general, adults need between 310 to 420 mg of magnesium each day. However, many people find it hard to meet these requirements.
This is because modern farming lowers soil nutrients, and food processing decreases magnesium levels.
Special Considerations for Various Populations
Certain groups may need more magnesium. For example, pregnant and lactating women need more magnesium for the baby’s growth and milk production. Also, older adults might need more due to changes in how their bodies absorb and use magnesium.
Those with anxiety, depression, or mental health issues may need extra magnesium too. A healthcare professional can help decide the right amount for you, based on your specific needs.
| Population Group | RDA (mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Adult Men (19-30 years) | 400 |
| Adult Men (31 years and older) | 420 |
| Adult Women (19-30 years) | 310 |
| Adult Women (31 years and older) | 320 |
| Pregnant Women | 350-400 |
| Lactating Women | 310-360 |
| Older Adults | 400-420 |
Incorporating Magnesium into a Holistic Treatment Plan
Addressing anxiety and depression often needs a mix of strategies. Adding magnesium into your holistic treatment can make a big difference in mental health. It helps to understand how this essential mineral improves emotional well-being. This opens doors to natural remedies for anxiety.
Complementary Natural Anxiety Remedies
With magnesium, other natural anxiety solutions can boost mental and emotional health. Mindfulness meditation, regular physical activity, and enough sleep build a strong mental health foundation. These practices work well with magnesium, leading to a thorough method of improving well-being.
Dietary Sources of Magnesium for Anxiety and Depression
The right diet is key for enough magnesium. Many people don’t get enough, risking deficiency that worsens anxiety and depression. Good magnesium sources include:
- Leafy greens like spinach and kale
- Nuts and seeds such as almonds and pumpkin seeds
- Legumes, including black beans and chickpeas
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice
- Fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel
Eating these foods daily helps meet magnesium needs and boosts mental health. For more on self-care routines for depression, check out this guide.
Using magnesium with a balanced diet and self-care can manage anxiety and depression well. Focusing on magnesium-rich foods keeps this crucial nutrient at optimal levels. This supports emotional stability and resilience.
Conclusion
Magnesium plays a big role in our mental health, especially for anxiety and depression. It helps people make smart choices for their wellness. Research shows it’s good for mood and stress relief, so it’s key for feeling mentally well.
Adding magnesium-rich foods and supplements, like magnesium glycinate, to your diet can help fight depression. This combo can truly make a difference. In fact, studies show they can improve anxiety and depression in just weeks. That’s why it’s worth considering magnesium for better mental health.
Talking to healthcare pros is important for personalized advice. Magnesium is getting more attention for its mental health perks. For more details on magnesium and mental health, check out this study.